The most popular type of supporting structure among private developers is the foundation using Tise technology. The abbreviation TISE means Technology of Individual Construction and Ecology. Tise technology allows you to build a house with your own hands without experience in construction and in the absence of qualifications.
To build a foundation using Tise technology means saving almost 2 times the family budget allocated for building a house and also saving money during the further operation of the house.

The TISE foundation allows you to save money during construction and, at the same time, does not harm the environment.
When using this technology, the environment does not suffer, since the construction of the house is carried out using available raw materials. The following tasks are solved with Tise technology:
- insulation of premises from contact with materials for building a house;
- the possibility of using effective ventilation, which avoids the appearance of stagnant unventilated zones in the house, the introduction of displacement ventilation schemes;
- the ability to create a favorable electromagnetic field;
- does not create increased background radiation;
- reliable insulation of structures from the penetration of radioactive elements, in particular radon gas, is ensured;
- introduction of a new energy saving system that reduces the energy level from heating systems by 2-3 times;
- the ability to ensure the environmental safety of a residential building.
Advantages and disadvantages of the foundation
The foundation built using the Tise technology is a pile-tape structure, which is made in the form of a pile field. The connecting pile does not touch the ground. This property of the structure eliminates soil pressure on it at any time of the year.
The chise foundation has the following characteristics:

- reliability;
- efficiency;
- ease of installation;
- short construction time;
- the possibility of constructing the structure in winter;
- environmental friendliness;
- possibility of use in seismically hazardous areas;
- leveling of any vibrations;
- possibility of construction at any groundwater level.
The chise foundation consists of the following elements:
- reinforced piles of special shape;
- reinforced concrete grillage.
Piles for the Tise foundation have a hemispherical expansion at the bottom. This expansion allows you to increase the support area and improves the load-bearing characteristics of the foundation of the house. This feature of the supporting structure allows it to be used in the construction of different types of houses. This foundation does not shrink and is suitable for both light frame houses and stone houses.

The spherical part of the pile structure has a very useful property: it resists the extrusion forces that occur on heaving soils and maintains support in the ground.
Disadvantages of building a foundation include the need to purchase professional equipment: drills or motorized drills.
The grillage is a strip part of the Tise technology, made of reinforced concrete. The grillage is made at some distance above the ground. The presence of a gap between it and the ground does not allow heaving forces to affect the foundation.
Return to contents
Economic component of the supporting structure
The construction of a column-and-strip foundation using the Tise technology is also advisable from an economic point of view. It is characterized by a small volume of excavation work and lower costs for the production of concrete mortar, since when making a supporting structure of this type for a house, less of it will be needed than for an ordinary strip foundation.
Construction of a foundation using Tise technology allows you to save money and build a structure in a short time; for its construction it is not necessary to attract additional labor.
Return to contents
Installation of a column-strip foundation

Installation of foundations using Tise technology requires a preliminary calculation of the number of piles and determination of their exact location under the grillage, taking into account the load-bearing characteristics of the soil and the design of the house. It consists of the following steps:
- contour marking;
- drilling and expansion of wells;
- reinforcement of piles;
- grillage production.
These calculations are entrusted to specialists from design organizations, since it is necessary to conduct a study of the soil on the site, calculate and prepare a construction project.
Scheme for marking the foundation according to the Pythagorean theorem.
- First, 2 enclosure boards are hammered in. They are installed at a distance from the length of the future wall, increased by 2 m. A cord or fishing line is attached to the boards. The cord material should not stretch, so fishing line or twine is more often used. The first angle is determined by retreating 1 m from the outer board, and a peg is driven in. From the first peg, measure the length of the wall of the future house and drive in a second peg, this will be the location of the second corner. Extension boards are installed to indicate the zero level of the building in the TISE foundation; it corresponds to the upper level of the grillage. Using a hydraulic level, check that the top edge of the board coincides with the zero mark.
- To mark the 2nd wall of the foundation, a right angle should be determined perpendicular to the first. This can be done by applying the Pythagorean theorem or the Egyptian triangle principle. According to the Pythagorean theorem, knowing the dimensions of the walls of the house, you need to calculate the diagonal. At the first point, a cord longer than the length of the 2nd wall is attached and stretched between the railing boards. From the 1st point, the length of the 2nd wall is measured and the 3rd peg is driven in. At the second point, a cord equal to the diagonal of the triangle formed by the walls is attached; it is connected at the 3rd point with the cord from the first point. If the cords are well tensioned and do not sag, then at the first point an angle of 90º is obtained. When using the “Egyptian triangle”, measure 12 m of cord and tie it into a ring. At a distance of 3 m the 2nd knot is knitted, after 4 m the 3rd knot is knitted. The distance between the 1st and 3rd nodes will be 5 m. Using the resulting triangle, a right angle is fixed on the site of the future foundation. To do this, place a knot at the marked point, which is located between the sides of 3 and 4 m, 2 other corners are spread to the sides along the future walls, with an even tension of the cord along the sides, a right angle is obtained.
- Repeat the steps to determine the right angle for the 3rd wall, hammer the peg into the 4th point. Connect the 3rd and 4th points with a cord, creating the outer contour of the chise foundation.
- Internal casting is carried out by measuring from the corner points a distance equal to the width of the grillage, hammering in the pegs and connecting them together with a cord or fishing line.
- The locations for drilling wells for piles are determined. The centers of the wells will coincide with the line located in the middle between the cast-offs; a cord is pulled along this line. The places for drilling corner wells at the intersection of walls are marked with pegs.
Along the perimeter of the walls, the locations for drilling wells are determined according to the step calculated by the design organization, and they are marked with pegs.
Return to contents
Drilling and expansion of wells
In the places marked for wells, they dig holes half a shovel deep and begin to drill. Wells are drilled using a TISE drill. This is a hand tool consisting of a handle, a drill, a two-section rod, a soil accumulator and a folding shovel. The drilling depth is adjusted by a rod. The soil intake and loosening is ensured by the soil receiver, and the folding blade leads the process of expanding the lower part of the well.
To optimize the drilling process, experts advise drilling 5-6 wells and then expanding them, this will save time on drill conversion.
To improve the sand drilling process, experts advise pouring about 5 buckets of water into the well overnight. This will make the expansion easier the next morning.
When drilling expansion, the drill and rod must rotate, a folding blade is put on the rod and secured with a pin to the soil receiver. The shoulder blade is raised using a cord, and it lowers itself under its own weight.
Having completed the expansion under the support, reinforcement begins.
Construction of houses on stilts- this is, in some way, a classic method of house building in many countries of the European region, which has successfully reached Kamchatka. Pile foundation technology has been and is used to this day for the construction of country houses and cottages.
Wooden piles
For the manufacture of wooden piles, mainly hard wood species are used, such as oak, larch, ash; in rare cases, pine is used due to its increased resin content.
For a longer service life in the ground, the wooden pile is subjected to heat treatment or treated with bitumen impurities with anti-septic tanks. It should be taken into account that the wooden pile is not installed under massive buildings, but under small wooden country houses or outbuildings. With this treatment and application, piles can last from 20 to 30 years. Such indicators provide an opportunity to create budget housing. When calculating the number of piles, all angles around the perimeter of the building are taken into account, the distance between piles is calculated within 2 meters. The most common size of a wooden pile is 120x150 cm.
Screw metal piles
The screw pile, thanks to its special design, is maximally adapted to both compression and pull-out as the load increases.
According to its characteristics, the steel screw pile copes well with frost heaving of the soil, therefore it is mainly designed for installation in soft, water-logged soils and is not suitable for installation on rocky rocks.
Construction of a wooden house using screw piles has a number of advantages over strip foundations:
- saving the developer money and time
- carrying out construction work on problematic soils
- no need for careful site planning
- possibility of building a wooden house on rough terrain
- reliability of home protection from temporary natural disasters
- construction work is not limited to the seasonal period
- if necessary, installation of piles can be done manually
Bored piles They are widely used in the construction of buildings and structures due to the speed of installation and the execution of work in winter.
What is the most important thing in building a house or any other building? Quality of the material? Construction plan? Interior or exterior? Of course, these points are very important. But the construction of any structure begins with foundation. After all, even if the house is built from the most expensive and high-quality materials, and the most professional engineers work on the construction plan, the house will collapse if the foundation is laid incorrectly.
What is it foundation?
Foundation- this is a part of the structure that is installed in the ground to distribute the load of the building onto the base. Thanks to this, subsidence of the structure is eliminated and prevented, which can lead to the destruction of the entire structure. If foundation installed with high quality, the building can withstand wind, water, earthquakes, vibrations from transport, etc.
Kinds foundation
There are many types of foundations. It all depends on the terrain on which the structure is being built. The varieties include:
- Tape;
- Monolithic tape;
- Columnar;
- Pile;
- Shallowly buried;
- Slab;
- Floating;
- Screw.
It is also worth noting that to build a bathhouse, cottage or fence - cheap foundations will be different, even if they are built on the same territory. For example, if the dacha is wooden, then a shallowly buried one is suitable for its construction. cheap foundation, columnar or monolithic, in the presence of underwater water and for large-sized structures, a pile foundation is suitable.
What to consider when bookmarking foundation?
When laying the foundation, many factors must be taken into account so that the structure does not collapse in a couple of years or even months. So, during construction you need to consider:
- Climate;
- Temperature;
- Humidity;
- Seasonality (rain, snow, scorching sun);
- Flood risk;
- Windiness;
- Presence or absence of vegetation around the perimeter;
- The place where the structure will be located (lowlands, hills);
- Underwater;
- Priming;
- Availability of roads;
- The immediate purpose of the building;
- Height and weight of the structure;
- The weight of the furniture that will be in the rooms;
- Number of storeys.
What to make a cheap foundation from?
Foundations are made of concrete, brick, stone, gypsum concrete, crushed stone, slag concrete, cement, metal structures, wood, sand, as well as various insulation materials. Again, it all depends on the climate, type of structure, construction time, budget (different foundations require different amounts of materials and costs). For example, if you take a strip foundation to build a house, you need a lot of different materials (concrete, sand, wood, reinforcing steel, insulation), but to build a foundation for a fence, you need much less materials, at least because of the smaller area of the structure.
Foundation of the building- this is the basis of the entire structure. Without it, any structure will not stand. If the foundation is of poor quality, the structure will sooner or later collapse. It is important to remember that during construction we are talking not only about money and time costs, but also about safety. Therefore, it is better to entrust this matter to professionals.
Bored piles are cylindrical reinforced concrete structures often used in the construction of buildings and structures. The basis of any bored pile is a reinforcement cage, which is responsible for strength. Thus, reinforcement is necessary to increase the load-bearing capacity: concrete perfectly withstands compression loads, but with tension, which occurs in the lower part of structures, it is more difficult. It is this tensile load that is placed on the reinforcement frame in the bored pile; this saves buildings from subsidence and cracks in the walls. The second component of a bored pile is the concrete body. We all know well that the strength of reinforced concrete houses is an incredible phenomenon, as the people say: “You can’t drill anything, you can’t pierce anything.” The fact is that with the help of reinforcement, quite a long time ago, they learned how to create a kind of “alloy of concrete and iron” - this is a durable reinforcement frame filled with concrete. When this material is used correctly, no expense is spared and a rational waterproofing treatment is created, then reinforced structures are virtually eternal. In the case when, according to the design of your house, we will have a pile-grillage foundation, a grillage with a low depth of 5 cm. Laying such a foundation begins with the installation of bored piles; the first step to the production of bored piles is the production of a reinforcement frame. In this case, the reinforcement frame of each pile consisted of 4 ribbed reinforcement rods, which were connected every 40 cm with clamps, also made in-house.
According to technical recommendations for constructing foundations from bored piles, the diameter of the reinforcement cage should be 140 mm less than the diameter of the well to avoid jamming. On the outside, the frame must have limiters (clamps) that provide the required thickness of the protective layer of concrete.
Frame reinforcement for bored piles is considered to be a structure made from metal reinforcement. Usually it is created from rods for different areas of reinforcement of reinforced concrete elements. The reinforcement cages used for the pile foundation and grillage are connected using oblique and transverse rods, or special clamps, ultimately creating an all-metal structure. Before you begin to create such a frame for bored piles and grillage, you should make a careful calculation according to which to prepare the line.
Most often, reinforcement of piles using cage-type frames is used in the construction of large-scale industrial buildings and structures that involve pouring concrete in large quantities.
Flat frames - several longitudinal layers of mesh, welded using rods. In this case, the longitudinal rods are additionally fixed using transverse or oblique rods.
The entire process of manufacturing a reinforcement cage for bored foundation piles can be divided into the following stages.
Preparation of reinforcement for piles. Let's say you purchased eleven-meter ribbed reinforcement with a diameter of 12 mm, from which 3 rods were made using a grinder and the most ordinary marker. For the required quantity of 144 pieces, 48 rods of 11 meters each were purchased. To make 288 clamps, smooth 6-meter reinforcement with a diameter of 6 mm was used, the calculation was done in a similar way. Calculation is necessary in order to determine the size of the piles and the diameter of the reinforcing elements. Reinforced frames are used to reinforce the pile-grillage foundation at the stage prior to pouring. Provided that the calculation is carried out correctly, this allows to increase to some extent the strength of the product and the degree of its resistance to various mechanical loads.
Making a wooden template for assembling piles, namely fixing longitudinal reinforcement. We fasten 2 wooden boards with self-tapping screws. We mark 4 holes on them according to the dimensions known to us (the sides of the clamp), ours were 15 cm each. We drill.
Manufacturing of clamps. To speed up the process, we purchased a manual arma bender; this is a simple device for quickly bending reinforcement. With its help, we easily, although not very quickly, made 288 clamps
We find a place to make the reinforcement cage. On the site we built 2 simple wooden structures on which we could easily lay longitudinal reinforcement and attach clamps to them without any problems.
Classic reinforcement frames for piles are a knitted or welded structure made from reinforcement of various diameters. The frames follow the shape of the future concrete product and are divided into flat and spatial. Flat frames are more often called reinforcement meshes. The degree of saturation of reinforced concrete products with steel reinforcement is called reinforcement density and is characterized by the ratio of the weight of the reinforcement to the volume of concrete in which it is contained. Reinforcement of critical reinforced concrete structures requires a density of 500-600 kg/m3.
Transverse reinforcement with clamps. For each pile we needed 8 clamps with a pitch of 40 cm. After the clamps were placed on the longitudinal reinforcement, we placed a wooden template made in advance. We knit the reinforcement using knitting wire, homemade clamps and a screwdriver with a hook.
Round reinforcement cages are widely used for reinforcing bored piles.
The production of reinforcing cages for piles is carried out automatically, by welding load-bearing reinforcing bars with reinforcement wound in a circle.
The main operating principle of the equipment for creating round reinforcement cages is to create a spiral (in automatic mode). For this purpose, reinforcing wire from a coil is used. Winding is carried out in a programmable step, directly onto longitudinal reinforcing bars pre-installed in the unit.
Frames of bored piles.
To create the frame of a pile-grillage foundation, the following materials will be required:
- hot rolled wire rod;
- smooth reinforcing bar;
- grooved reinforcing bar;
- special wire;
- coil corrugated fittings
- coiled smooth reinforcement
In some cases, metal rods are additionally coated with a special anti-corrosion compound. But more often they initially prefer to use products made of low-carbon steel, which, according to their characteristics, are not susceptible to corrosion. The production of reinforced frames for bored foundations can be carried out by both enterprises and specialists at the construction site.
Various approaches make it possible to make not only frames of standard shapes, but also individual ones, calculated for a specific product. In the latter case, a carefully prepared drawing is required to complete the work.
There are two technologies for manufacturing frames for reinforcing foundation piles and grillage:
- automation of assembly at the enterprise;
- manual assembly.
Frames for pile foundations
Typically, to solve problems such as reinforcement of piles and foundation grillage, a round reinforcement frame is used. Reinforced frames are especially in demand during the construction of residential and industrial complexes, as well as all kinds of specialized buildings and structures. At the same time, at the stage of pouring the foundation, standard reinforcement frames for piles are necessarily used, and floor beams are made from three- and tetrahedral frames.
The use of bored piles is most often practiced when constructing the foundations of buildings with a significant depth of solid soil. The advantages of using frames made of reinforcement for a pile-grillage foundation are completely obvious:
reduction of time spent on installation during the installation of reinforced concrete structures;
- reduction of work cycle;
- possibility of using waste reinforcement for work;
- increased performance;
- increasing the level of production profitability.
Modern engineers and builders prefer to use two types of frames, including reinforcement frames for bored piles:
Volumetric;
Flat.
Volumetric frames can be square or round. According to SNiPU, such frames are used to strengthen bored supports. The cross-sectional diameters of such metal structures, as a rule, range from 8 mm. up to 12 mm., the diameter of the pile must be stable - 0.3 m. Volumetric frames for bored supports are actively used when pouring particularly large masses of concrete mortar. The frames themselves are usually made using welded gratings. There should be from 3 to 10 grids.
Flat reinforcement cages are products that are actively used for construction purposes during the reinforcement of linear reinforced concrete structures. The use of a flat reinforcement frame significantly reduces the cost of work performed, while increasing the strength characteristics. After all, cracks cannot form in such a structure, and the likelihood of deflection is reduced to zero.
Flat frame structures consist of two and three longitudinal layers of reinforcing mesh connected by rods. SNiP requires that the rods be connected to each other using other rods of a transverse, inclined or continuous type.
Pile frames are often used to erect buildings next to already built houses. This allows you to significantly reduce the dynamic load when laying a new foundation. The use of bored piles when creating a foundation allows the use of point construction techniques in places where the use of other technologies is impossible or difficult.
The use of round reinforcement cages allows you to increase the speed of installation of reinforced concrete structures, reduce the cycle of production work, and get rid of waste reinforcement.
The main material used for the manufacture of reinforcement frames is special wire VP-1, as well as smooth or hot-rolled wire rod, smooth and corrugated reinforcing bars, corrugated coil reinforcement, the diameter of which is 6-12 mm. The correct proportions of individual components allow you to prepare a strong and reliable product that will fully meet all the necessary operating requirements.
A few words about creating the lattice and frame. Welded type gratings are connected to each other using metal rods oriented perpendicular to the plane of the grillage.
It should be noted that such frame structures are suitable for supports of any diameter. SNiP allows you to change the shape and adapt it to the required production method. The frame, which has particularly large dimensions, is carried out individually; the frame for the bored support must be manufactured using automated welding lines.
In many Russian cities, construction sites have restrictions on the use of driven piles; foundations are built using bored pile technology. A bored pile is made directly in the ground. A reinforcement cage is installed into the drilled well and concrete mixture is poured. After the concrete has hardened and reached its design strength, the pile can bear the design loads.
Frames of bored piles can be used for the construction of buildings for various purposes: industrial, residential or public. The use of this type of piles is possible on almost all types of soil, with the exception of rocky and coarse soil.
Bored piles are a technology used in the construction of buildings and structures with deep foundations - multi-story industrial and residential buildings, road junctions, supports for bridges, overpasses, etc., when there are large concentrated horizontal and vertical loads, as well as under difficult construction conditions.
Bored piles are holes into which various types of metal frames can be lowered. Concrete, sand-cement mixture or water-cement mortar is pumped into wells under pressure.
Bored piles are installed without the use of casing pipes in low-moisture rocks. In this case, drilling can be carried out without fastening the borehole walls. In water-saturated rocks, bored piles are installed only under the protection of casing pipes or polymer or clay drilling fluid.
Bored piles are formed from cement, the setting period of which must be at least 2 hours. The mobility of the concrete mixture is ensured by selecting its composition and introducing surfactant plasticizing additives into the mixture.
Strip and column foundations are more traditional and understandable for the construction of baths in Russia, however, the more modern bored foundation has a number of advantages over them. And for areas on slopes and with problematic soil, this is an ideal option. And for those places where the development is especially dense, a foundation on bored piles allows you to build even a two-story bathhouse or house without consequences for the soil and nearby buildings.
Bored piles, made without the use of casing pipes, are made in the following way: a well is drilled in the ground using a rotary or impact drilling method. During the drilling process, a clay solution is used, which will compress the walls of the well, thereby preventing the possibility of collapse. Also, with the help of an upward flow of this solution, particles of drilled soil are carried to the surface. After this, a reinforcement frame is lowered into it, which can be installed either along the entire length of the pile, or along part of the length, or at the very top to connect it with the grillage.
After this, the well is concreted using a pipe, which is moved gradually upward. When lifting a concrete pipe during concreting, you must always remember and ensure that its lower end is recessed into the concrete mixture by at least a meter. The concrete mixture fed into the pipe is compacted using a vibrator, which is fixed to the concrete pipe. Another concreting method involves using a mixer with a concrete pump. The pump pumps concrete into the well, and the concrete pipe always remains in the same position and is removed only after concreting is completed. This concreting technique eliminates the possibility of the pile being pinched by soil, while ensuring high quality concrete coverage.
Bored piles made using casing pipes are made in this way: a well is drilled into which a pile frame-pipe is installed. At the same time, the casing pipe allows you to cover the horizons of quicksand soils, and also ensures safety during piling work, helps control the main parameters of the borehole and ensures high-quality filling of the well with concrete.
Construction implies strict adherence to technology. Even small miscalculations will lead to consequences; first of all, the strength of the future structure will suffer. In order to avoid such a truly sad event, you need to know the sequence of actions.
Foundation calculation:
The width of the foundation should be based on the thickness of the future walls. This means that the frame structure should not have a powerful zero level, because the walls will be light and thin. If you are going to build a real Russian steam room from timber, then in order to make the foundation with your own hands you will have to make it 40 mm larger, because the most important thing is to evenly distribute the load over the entire area of the foundation.
Markup:
It is necessary to understand that the piles can be placed in almost any order; the most important thing that needs to be ensured is the uniformity of the load. If you are going to make a uniform load, then the piles can be placed as a solid wall, in a checkerboard pattern, or under certain areas of the bathhouse.
One well is completed in about a few hours. This means that it will take quite a long time to drill several holes for piles, but how can you save precious hours? Everything is quite simple, you need to use the most productive hole drills. It is believed that models from Japanese and Korean manufacturers are the most reliable and fastest. Therefore, if you decide to save time, then sacrifice money and everything will be done in the shortest possible time.
Formwork:
To continue building the foundation, you will need to create the formwork that is necessary to create a well. Formwork is necessary in those regions where the soil is not dense, which means there is a high probability of crumbling. If the geological conditions are normal, then you can easily do without creating formwork, that is, concrete should be poured directly into the well, which makes the process much easier. The main thing to remember is that you will need a small formwork on the surface; it will serve as the head of the pile. Such formwork can be used as roofing material rolled into a tube.
Selection of piles:
Piles must be selected so that they serve for many more years. The load-bearing capacity must be much better and more reliable than that of driven piles. It is the simplicity of the designs of bored piles that can limit excavation work; accordingly, it is not necessary to make a large number of piles; they cannot even be installed on every square meter.
Making piles is a fairly easy process, which means you can do everything yourself. This doesn't require anything special. The most important advantage of making piles yourself is that you don’t need to think about where to store the piles. Bored piles are very popular in construction, the base of which has a diameter of 50 cm, this allows them to hold approximately five tons of weight (each pile holds 5 tons of weight). Such a foundation can support a solid bathhouse made of brick, which will contain a variety of architectural delights.
As for the manufacture of piles, almost any material can be used, everything depends only on the quality of the soil, which prevails on the site. For example, if the soil consists of clay and there is a lot of water in it, then in order to install piles you will have to strengthen the wells with special casing pipes, but if the budget does not allow, then you can limit yourself to a clay solution. Thanks to this method, the soil horizons will be blocked, and the foundation will become safe. It must be taken into account that the depth and width of wells are subject to deformation. This means that in order to ensure the durability of the foundation, it is necessary to seriously think about how to withstand deformations.
"Pillow":
A “cushion” for a foundation made of bored piles is strictly necessary for structures of this type. Most often, the pillow is made using sand, crushed stone or concrete mixture. The pillow must be compacted well, and then the well must be filled with the main material, which will ensure the rigidity of the structure.
Foundation reinforcement:
In order to give additional strength to the piles, reinforcement is most often used, which is firmly poured into a single structure with the help of a grillage. In order for the piles to be strong, it is necessary to think in advance about the production of reinforcement cages. In order to do this, you will need several rods with a diameter of approximately 12 mm, which are connected in a special way. You can use them as a finished frame, but if you don’t have time to bother with manufacturing. Then you can use triangular frames, which are usually used for floors.
At this stage, the piles are prepared. It is necessary to understand that the thickness and location depend only on the rental of the bath. To determine the length, you must use either a hand drill or a power drill.
The depth of the piles cannot be less than 1.5 meters and greater than the depth of soil freezing. However, you need to know that the pile must necessarily go 15 cm more than the depth of soil freezing in a particular area allows. It is for these purposes that a foundation calculation is needed. The depth of freezing can be determined from geological maps, and if this is not possible, you will have to consult with specialists. It is very important to follow all calculations; if the piles are below the freezing depth, then the foundation will not be “squeezed out” as soon as snow falls.
A very important point: about half a meter of piles should remain above the surface. They will be filled with concrete, and after it has cooled, the piles must be finished with roofing felt and connected using strapping.
Pouring concrete:
At this step, the installation of piles is completed. All you need to do is pour the concrete. The most common method is to pour concrete from a mixer. In this way, you can pour a large amount of concrete very quickly, leaving a lot of time for other work.
Filling should be done only with quick-hardening cement, which is diluted in small portions and each time the compaction occurs exactly the same as the previous time.
The idea of this miracle foundation is that the piles are not driven into the ground with force and do not damage the layers - they seem to “grow” out of the ground. In simpler terms, a well is drilled in the soil, a pipe is placed in it or removable formwork is formed, and the whole thing is filled with mortar. And for weak soils, a bored foundation with a grillage is the only possible option. After all, the main task of any piles and pillars is to rest on the hardest layer of soil - the incompressible one, the one that is always below the freezing level of groundwater. And due to the geology of some regions, it may be located quite deep. It is precisely the bored piles that reach such a line - holding the entire newly erected structure on it. Today, a more expensive but reliable zero level is also practiced, such as a pile foundation on bored piles with insulation. For this purpose, polystyrene foam is used, which, as is known, has a rigid structure. It is fixed directly onto the waterproofing and covered with soil. In addition, polystyrene foam itself is an excellent shock absorber for soil heaving forces. The main thing is that even a strip foundation on bored piles does not disrupt the communications that were previously installed on the site. And the fact that a basement in such a building cannot be built later cannot be considered a problem. The good news is that the service life of such a foundation is 70-100 years.
A bored foundation is the foundation of a house, one of the types of pile foundations that any craftsman can easily equip on his country site for building a house. Quite a lot of people have no idea what a bored foundation is. You won't hear any versions. But in essence it means drilling a hole in the ground, installing reinforcement and pouring concrete (filling). That’s why they are called bored piles – because they are drilled and driven. In most cases, when they talk about a bored foundation, we are talking about bored piles as an element, for example, of a pile-strip foundation. Naturally, you can use bored piles directly as a foundation, without tying them with a concrete tape, for example, for a fence, change houses, sheds or a small bathhouse, but for a private house it is more justified to use a pile-tape or pile-grillage foundation, in which all these piles are rigidly connected between each other with a concrete strip (grillage). This tape, firstly, distributes the load between the piles, secondly, it rigidly connects the entire structure of the future building and thirdly, it forms the foundation for the load-bearing walls of the house. All the charm of purchasing a plot for the construction of a country house in a well-located and picturesque place, near a river or lake, can be overshadowed by very complex geology and soil hydrology. And despite all the attractiveness of the area, until recently people were reluctant to build on sandy quicksands, slopes or soils with high groundwater levels. The bored foundation will not disrupt the communications that were previously installed on the site, so you can use them when building a house. Problems of house stability on soft soil today can be effectively solved with the help of a bored foundation. This kind of foundation can be used in places where groundwater is close to the surface of the earth. For places with problematic soil, such a foundation is a real salvation; no other foundation has the ability to rest on denser layers of the foundation. And the bored foundation fulfills this task “one hundred percent.” Such a layer can be located very deep, where bored piles are reached. When constructing a bored foundation, supports are poured, they adhere to the soil with the side surface and partially the base of the pile, without deformation of the soil rocks, and when driving reinforced concrete piles, the soil layers are compacted, creating the so-called load-bearing or support core. Today, a bored-type base with insulation, which is used as polystyrene foam or expanded polystyrene, is becoming increasingly popular. The difference from a pile foundation is that there are a lot of advantages for arranging a bored foundation: there is no need to level the soil or make a pit, ideal for uneven terrain; quick installation (depending on the soil); there is no need to purchase expensive piles, low cost; there is no need to drive the structure into the ground using a piling machine - wells are drilled in the ground, after which the wells are filled with concrete mixture. This foundation is columnar with a circular cross-section, due to which the lateral surface of the piles becomes minimal and the support area is maximally large. Often, pipes made of: thick steel are used as support - a material that is more durable and resistant to mechanical stress; made of asbestos cement - a material that is resistant to corrosion. To construct a bored foundation, the required quantity of concrete or the necessary dry components for its preparation, steel reinforcement and waterproofing materials are purchased. The size of the piles and the depth of the well can be increased if, during the construction of the foundation, a deeper occurrence of supporting rocky layers is discovered, on which it is planned to install supports.
There are several types of bored foundation:
The foundation on piles is called pile-tape or pile-grillage. Such a foundation is made on ordinary piles, without expansion at the bottom, and then the strip must be made recessed in order to increase the area of support on the ground. This is one of the types of shallow foundations. Its main disadvantage is that even though the pile is buried below the freezing depth, it can still be lifted by frost heaving due to pressure on the shallowly buried tape.
You can use piles with an extension at the bottom. The support area of such a pile is six times higher and therefore there is no need to bury the tape. Depending on the bearing capacity of the soil, a bored pile with an expansion at the bottom carries a load of 10 to 35 tons, and if there are 30 to 100 such piles, then, accordingly, they will withstand even a brick house with concrete floors. These calculations are approximate and loads must be calculated individually in each specific case. Supporting the house on a pile with expansion makes it possible not to bury the fly, as a result of which frost pressure on the tape is eliminated, the gap between the tape and the ground compensates for frost heaving and the house stands firm.
Another type of foundation on bored piles is free-standing piles without a concrete strip; they can be tied with a channel or wooden beams; you can also simply put some small structure on the piles. Free-standing bored piles, not tied with a common concrete tape, can deviate from the axis and undergo various movements. Strapping made of metal or wood is cheaper at the initial stage, but these materials are susceptible to corrosion and rotting and are quite flexible
When constructing a bored foundation, it should be taken into account that two types of loads act on piles:
Compression - occurs as a result of the impact of the mass of the structure on the base;
Tensile - The bottom of the pile is firmly fixed in the depths of the soil (in stronger layers), and the upper part is pushed out by heaving soils located closer to the surface (this usually happens in the cold season).
For example, when using M100, a pile with a cross section of 200x200 mm will be ready to withstand pressure up to 100 kg/cm2. It turns out that the area of such a support will be 400 cm2 and can bear a weight of about 40 tons.
Before the process of installing a bored foundation, first of all, the site is marked out according to the existing site plan. To do this, determine the axes of the house and mark the first angle, from which the location of two adjacent walls is marked with a protractor and their length is measured. The remaining corner point is determined from the marked walls. Using stakes and rope, markings are made, marking the installation locations of future supports. It is very important to carry out the markings very carefully, since due to errors in the location of the pillars, the foundation may turn out to be unreliable. Only after marking can you start drilling wells for future supports. In this process, you can use both mechanized equipment and a hand drill. A hand drill can make a well from 15 to 45 cm in diameter, but it is worth considering that such work is very difficult to do and drilling takes a lot of effort. If it is not possible to determine the exact level of solid soil, it is recommended to use the average value for different areas, in which recesses are made to a depth of 1.5-2 m. Wells are drilled at least one and a half meters and 30 cm below the soil freezing level. Achieving strong soil layers is necessary to ensure that the piles do not shrink unevenly in the future, as this can lead to the destruction of the structure. After all the wells have been made, you need to make a kind of pipe from roofing felt, which will match the diameter of the well, and will be approximately 50 cm longer in length. The upper part of the pipe must be made of several layers and tied together with wire. Such a pipe will become the formwork for the pile. The finished pipe is placed in the well until it stops. If water rises in the well and fills it more than a quarter, it should be pumped out.
Next, the formwork is installed, only after which the reinforcement is performed. Craftsmen often do not install roofing felt formwork, but it is required for better strength and setting of the cement mortar. The formwork also protects the pile from soil heaving in the winter and prevents moisture from leaving the concrete and being absorbed into the surrounding soil. After the formwork is ready, you can begin to reinforce the future pile. A reinforcement frame is created from ribbed rods, the thickness of which ranges from 6 to 10 mm. Three pieces will be enough, which are connected by crossbars to each other every 60 cm. In the case of pouring a base with a strip grillage, it is necessary to bring the rods above the pile for ease of connecting them to the grillage. The additional height is taken from the calculation of the height of the grillage, which is 2–3 cm greater. For this, reinforcing bars (minimum diameter 8 mm) are installed in the formwork and tied with wire. The threshold level of the rods above the ground depends on whether the foundation will include a grillage in its design. If so, the steel rods must be raised to the height of the grillage to ensure the construction of a solid base. Having installed a bunch of reinforcement, you can begin pouring concrete inside. This is best done with a mixer, as it allows you to carry out large-volume work. Filling must be done with concrete that is capable of rapid hardening. Each layer must be processed with a deep vibrator to eliminate voids inside the mass. To make your work easier, you can dilute quick-hardening concrete in small portions while the previous layer is being compacted.
Conveniently, the foundation on bored piles can be built at any time of the year; you do not need to wait until spring to install it. But the work must be carried out in accordance with the technology so that problems do not arise that could harm the future structure and the building itself as a whole. A foundation on bored piles is the best solution for a lightweight structure. It will be indispensable on problematic soils and will help transfer the load to denser layers of soil. It is not difficult to make such a base with your own hands, but only if you strictly follow the installation instructions. Such a foundation is designed to last 70-100 years, when, to tell the truth, a brick foundation will last almost twice as long. Also, when using this foundation, it will be impossible to construct a basement and it is prohibited to build a bored foundation on moving soils. Also, the main disadvantages of the design include the labor-intensive installation process and the large volume of concrete work.
Bored piles are a method based on drilling a well and pouring high-quality concrete after drilling. The process of effective concreting occurs using reliable metal reinforcement. Such structures are built mostly in the field of suburban construction. Depending on the type of soil, durable formwork may or may not be installed. These are stable soils; there is no risk of walls collapsing during work. The concept of “cast-in-place piles” combines a very large number of different pile designs and methods of their manufacture. But for all types of cast-in-place piles, the basic technological scheme is fundamentally common: a well is constructed in the ground using one method or another, which is then filled with concrete. If, before filling the well with concrete, a steel reinforcement frame is lowered into it, then a reinforced concrete cast-in-place pile is obtained. Bored piles today are actively replacing conventional foundation supports. The range of use of these piles is very wide; they can also be used in the construction of multi-storey buildings using an industrial method, not only in the construction of private houses, bathhouses, etc. With the help of such a foundation, the construction of panel and frame houses, wooden cottages, bathhouses, gazebos, and so on is realized. This type of foundation is an alternative to a deeply buried strip foundation, and it can experience the same loads without any problems. The use of bored piles in the foundation of a frame house will reduce the cost of work by at least 2 times compared to the construction of a strip foundation. Bored piles are a current type of foundation support, made in the form of monolithic cylindrical structures with a reinforced reinforcement frame. Bored piles are an option for creating the foundation of a structure. Most often they are used to support tall buildings that have a strictly vertical load. The advantage of bored piles is that they can be poured with concrete directly on the construction site, when other types require only factory assembly. The ideal foundation for piles of this type is dense sand and soil with clastic rocks of medium-sized fractions. They are usually used for foundations of tall buildings or industrial structures that will have to support thousands of tons of weight, and most often in places with unstable or difficult soil for various reasons. The use of this kind of foundation has many positive aspects. So, we can say that the construction of foundations using bored piles is a technology that has long proven itself on the positive side. In terms of constructive meaning, placement in plan and work in the ground, there is a fundamental difference between concrete piles and soil piles. Concrete or reinforced concrete piles are rigid rods that make up the base part of a pile foundation. From such piles the load from the structure is transferred to the ground. The concept of “soil pile” is conditional. The purpose of the latter is only to compact the soil lying below the base of the foundation. Upon completion of the work on compacting the soil with soil piles, they actually cease to exist and, together with the compacted soil, form a more or less homogeneous artificial foundation. The more the material of soil piles in its properties and composition approaches the properties and composition of the soil being compacted, the more homogeneous the artificial foundation will be. In private construction, hand drills or motorized drills are used for drilling wells. All work is done manually. It is necessary to pay special attention to the properties of the soil; if you drill a hole for a pile in easily crumbling soil, then you need to install concrete formwork. A reinforcement cage is installed into the drilled hole and only then concrete is poured. In the construction of a private house, bored piles are laid to the depth of soil freezing and a waterproofing coating is created from roofing material or cellophane, and in industrial construction, hydraulic devices for draining groundwater are used. On soft soils (peat, marshy areas), as well as in cities, tusk piles are used to build foundations. Their use is determined by the specifics of the soil: the construction of other foundations is either technically impossible or economically infeasible. Only depending on the ground conditions, bored piles are installed in one of the following ways: without fastening the walls of the wells (dry method), using a clay solution to prevent the collapse of the walls of the well, with fastening the wells with casing pipes.
In private construction, when using bored piles, cost savings when laying a foundation are significantly increased, since it does not need to be dug and poured to the entire depth of soil freezing. With the correct calculation of bored piles, the foundation does not lose its load-bearing capacity at all; moreover, the load-bearing load can be increased by using thicker reinforcement bars and reducing the distance between the piles.
Bored secant piles are structures whose installation technology replicates bored pile elements. The difference is that the secant elements are mounted in increments of “zero”, that is, they represent a solid wall of structural bodies, it serves to provide a complete support for the soil. They are usually used for the construction of underground parking lots, tunnels, and passages.
Bored tangential piles - this type of foundation is used in the case of vertical and horizontal load on elements from nearby buildings and groundwater. Typically, this method is used during construction in limited space, as well as for fencing very deep pits, for cutting embankments in soils with hard coarse inclusions. The advantages of this technology are the following indicators: Possibility of carrying out work in densely built-up conditions; There is no need to arrange additional drainage or drainage; Making bored tangential piles is not difficult, both in terms of labor costs and time.
Before installing such piles, the construction site is first marked with pegs and a vein is pulled to mark the location of the piles. Next, the location of drilling the well is marked using a plumb line lowered from the vein to the ground. A peg is driven into the point. Then the veins are removed to create an area with precise markings for drilling holes. There is also a less labor-intensive way, if you take a bayonet shovel with an edge 10 cm wide, lengthen the handle so that it reaches the bottom of the shaft. This makes a good tool for cutting soil from the walls of a well to obtain the required diameter. To increase the bearing capacity of the foundation, reinforcement is needed. Reinforcement of bored piles is used to construct foundations in soils where there is a risk of instability and movement - such reinforced frames increase the tensile strength of piles. But it’s not difficult to make reinforcement: you need to take the required number of reinforcing rods with a diameter of 10-12 mm, fix the rods into the frame using tying wire or welding. All that remains is to immerse the casing pipe to the bottom of the well, fill 1/3 of the mixture, lift the pipe, compact the concrete, fill the mixture again by a third, not forgetting the reinforcement, compact it, pour a layer of concrete and top it off. However, it is worth remembering that the frames of bored piles made of rods are immersed in such a way that the rods for connection with the grillage come out.
The most popular methods for installing bored piles are:
Pile system using drilling method in casing inventory pipe.
Pile system using the continuously rotating auger method.
Method of percussion-rope drilling.
The work progresses in three stages. Bored piles are driven into the soil using special bored machines. Boring machines can usually drill the ground up to 50 meters (this is stage 1), then drive a pile when changing the nozzle (this is stage 2). Another advantage of using this type of piles: during their installation there is virtually no vibration or noise, which has a positive effect on the stability of the soil. The drilling method directly depends on the condition of the soil layers. If the place where the building is being erected has unstable soil, such as sand, silt, groundwater, gravel, etc., then bored piles must be reinforced with reinforced concrete, steel frame or other structures. After the pile is installed in place, cement is poured on top of it (this is stage 3), which further strengthens the entire foundation.
When constructing multi-storey buildings, a special technique is used to make a bored foundation, which is used to drill a hole for a pile in the ground. After which a welded frame made of reinforcing rod with a diameter of 12 mm is inserted into it. An important role in working with bored piles is played by the diameter of the reinforcing bar used, which bears the main load.
Next, the pile is filled with cement mortar and waited until it dries. This technology is safe for surrounding houses in the case of compaction construction, since it is not associated with work that leads to active vibration of the soil and destruction of loose layers. If necessary, during drilling without casing, a bentonite solution can be used, which is fed into the well being developed, washes out soil masses from it and settles on the walls of the cavity, forming a crust that prevents soil shedding. The technology for creating bored piles with a removable shell is carried out when working on problematic, moisture-saturated soils. The casing pipe, in this case, prevents the collapse of the well walls and isolates the cavity from groundwater. The casing must be dismantled after filling the well with concrete. The creation of piles with a permanent shell is used when working in clayey soils, sands and sandy loams with a high level of groundwater, which can destroy the body of the pile at the stage of hardening of the concrete solution.
The main advantage of cast-in-place piles is the insignificant absolute and relative settlements of structures. The use of cast-in-place piles significantly reduces the number of standard sizes of prefabricated elements. In addition, the creation of a “pile-column” unit, which is difficult when constructing foundations on driven piles, can be easily implemented in any variant of cast-in-place piles. This type of foundation work can be used in dense urban areas, as well as in industrial construction.
The foundation is the support of the entire house. A strong, immovable, solid and durable foundation is a guarantee that the building will last a long time and will not be subject to deformation, that is, cracks will not appear in its walls, and window and door openings will retain their original shape. A pile foundation has a higher load-bearing capacity than strip and monolithic foundations, and it is also cheaper. Depending on the diameter, a bored pile can support about 1.5 tons. To build the foundation of an average-sized building, several dozen supports are enough. The diameter of bored piles can reach one and a half meters, length - up to 40 meters. Made of reinforced concrete, such supports can withstand heavy loads. Pile-grillage foundation on bored piles is a combined type of foundation made of support piles formed in the ground by concreting wells drilled in the ground. The second part of this foundation is a grillage that distributes the load on the pile field. This type of foundation has a high load-bearing capacity and can be used to build large houses and private cottages from any materials. A bored foundation with a grillage is often used, as it is distinguished by its versatility. It can be installed even on the most seemingly difficult soil. This type of foundation is suitable for houses made of brick and aerated concrete. A grillage is a system of strip lintels or slabs that connect the pile heads to each other. The point of this design is so that the pressure exerted by the house can be naturally redistributed between the foundation elements. A grillage is the horizontal part of a pile-column foundation that connects pillars (piles) into a monolithic structure. In order for the foundation to perfectly withstand the loads on it, the grillage must be properly reinforced. To do this, a structure is created from metal rods in two rows, which are connected by vertical rods. Wooden elements approximately 35 mm thick are laid under the bottom layer of reinforcement. To ensure that the frame does not move during concrete pouring, it must be securely fastened. The width of the grillage is about 30-40 cm. It is important to take into account that the thickness of the walls should be less. The purpose of the grillage is to distribute it evenly and transfer it from the walls to the piles, then to the ground. In difficult soil conditions and during the construction of large buildings, this property of a foundation with a grillage becomes a key element that ensures the reliability of the entire structure. A bored foundation with a grillage allows you to build buildings on difficult soils: viscous, marshy, quicksand, heaving. A foundation on bored piles with a grillage is indispensable for construction on unstable, uneven and sloping ground. A foundation on bored piles is indispensable in seismically active areas, areas with extensive networks of underground communications, as well as in soils with high alkalinity, where it is impossible to use screw supports.
In order for the foundation to be strong and durable, a thorough calculation must be carried out before starting work. To begin with, calculate the permissible load of one bored pile. Its value directly depends on the size of the supports. For example, a support with a thickness of 30 centimeters can withstand a load of 1.7 tons, and with a thickness of 50 centimeters it can withstand 5 tons.
Driven bored piles are cut so that their heads are at the same height, then connected with a grillage. The grillage ensures uniform distribution of the weight of the building between all piles.
The second factor on which the permissible load depends is the material for bored piles. When calculating the foundation, you need to take into account both indicators: diameter and grade of concrete.
For example, a bored pile made of concrete grade M 100 can withstand a pressure of 100 kg per square centimeter, that is, a square support with a side of 0.2 meters should theoretically withstand a pressure of 40 tons.
When making such a calculation of the number of bored piles, it is necessary to take into account not only the bearing capacity of each of the supports, but also the strength of the underlying soil layer. The stronger the underlying layer, the fewer bored piles will be required. When making calculations, you need to take into account many factors: freezing depth, reinforcement safety margin, height of groundwater rise, length of reinforced concrete elements.
All these factors will influence the number of bored piles, their dimensions and the distance between supports.
The final calculation is the distance between the supports. It must be taken into account that the maximum distance between bored piles should be 2 meters.
It is not allowed to leave a distance of less than 3 pile diameters between two supports.
Only after completing the calculation of the technical characteristics of the supports and determining the distance between them can you begin constructing a foundation on bored piles.
There is a technology that allows you to pour piles directly on site, preparing concrete yourself - this significantly reduces the cost of building a foundation.
Independent installation of foundations on bored piles with a grillage is a completely feasible task. The technology itself usually does not cause difficulties.
The grillage can be made from various materials. Our experts strongly recommend using monolithic reinforced concrete for these purposes. This type of grillage is quite durable, performs its function perfectly, but unlike metal structures it is much more economical and can be quickly erected without the use of cranes.
Step-by-step guide to pouring a grillage:
1. Place the formwork for the grillage;
2. Place a frame made of reinforcement inside the formwork;
3. Concrete solution is poured into the formwork. The pouring technology is the same as when laying a strip foundation.
height - from 0.3 m;
width - from 0.4 m.
The grillage can be monolithic or assembled from ready-made blocks. A base with a monolithic grillage is more reliable and durable, as monolithic technology imparts rigidity. A monolithic grillage is better suited for independent construction, since it is much more convenient to pour liquid concrete in a continuous layer than to install heavy reinforced concrete blocks on piles.
The grillage can be of two types:
- suspended;
- in-depth.
A suspended grillage is suitable for massive and lightweight wooden buildings: log, lumber, frame.
Bored pile foundations with a suspended grillage are used if construction is carried out on soil, the top layer of which is subject to increased heaving.
First you need to calculate how many piles are needed to ensure that the structure is securely fastened. To do this, you only need to know the load-bearing capacity of one pile and the weight of the future structure. Knowing the load that will act on the foundation, you can accurately calculate the required number of piles. To calculate the load on the foundation, you need to add up the weight of the materials that will be used during the construction of the house. You also need to add the weight of furniture in the house and equipment, and the load from people and seasonal loads.
Technology for constructing a foundation with a suspended grillage:
- site marking;
- identification of principal axes;
- ground leveling;
- digging trenches;
- driving bored piles;
- waterproofing;
- formwork assembly;
- ventilation assembly;
- removal of formwork.
How long the construction will take depends on the nature of the soil, the length of the foundation and the dimensions of the grillage. The approximate construction time for such foundations is a week and a half. The amount of money spent directly depends on the perimeter, height and width of the grillage.
Foundations with a deep grillage are suitable for monolithic and brick houses; houses made of timber and logs can also be installed on them if the wall thickness does not exceed 30 centimeters. They are placed on sandy, clayey, sandy loam and loamy soils. The site may be flat, with a slight slope or uneven terrain.
Bored piles with a grillage: the technology is very simple and it is accessible for DIY construction. For such a foundation there is no need to remove the soil at all - the piles are driven into the ground using a special vibratory driver and a special hammer. The piles driven into the ground are cut to one level, connecting on top with a grillage to evenly distribute the load. Technology for constructing a foundation with a deep grillage:
- site marking;
- identification of principal axes;
- ground leveling;
- digging a trench;
- backfilling a sand cushion with a thickness of at least 20 centimeters;
- laying geotextiles;
- pouring mortar for the grillage;
- installation of fittings;
- insulation of piles with roofing felt;
- removal of formwork.
Building a foundation with a recessed grillage takes the same amount of time as building a foundation with a suspended grillage.
It is useful to know that the reinforcement of a slab grillage is carried out in the same way as the reinforcement of a concrete slab, that is, two belts are made - at the lower and upper plane. Also, as a reinforcing element, you can use a reinforcing mesh made of ribbed reinforcement, the pitch is 25-40 cm. The upper and lower chords are connected using vertical rods. The strip foundation type involves a grillage made from a channel or I-beams. The main factor on which the choice of grillage type depends is the depth of winter heaving of the soil.
The main advantages of a bored foundation with a grillage are that there is no need to create a pit. There is no need to level the soil on the site. That is why such a foundation is often chosen by owners of plots with large differences in height of the soil surface. If a strip foundation is created on such land, this requires significant effort to prepare the surface. Fairly low cost. The described type of foundation will cost about half as much as a monolithic foundation. High speed of base installation. The described type of foundation can be created within 12-18 hours. In this case, such a base needs to stand for about 8-10 days. It is worth noting that the strip foundation must settle for about a month. There is no need to find an additional place where the piles need to be placed, since they are created at the construction site. No additional waterproofing required. Let's be honest, this also has its drawbacks - the main one is that the service life of such a foundation is approximately 70-100 years. But if a brick base is created, it can be used twice as long. With this type of foundation it is impossible to create a basement or cellar. Therefore, most often such a base is used during the construction of a summer house or bathhouse. Weak load-bearing capacity. Such a foundation is often created for one-story buildings. Inability to use a bored base on moving soil.
A foundation consisting of TISE piles costs two to three times less than other options, and the low cost in no way affects its quality and safety.
The peculiarity of this design lies in the shape of the TISE pile: in its lower part there is a hemispherical widening. This shape of the TISE pile helps to increase the bearing capacity of the foundation and prevents its extrusion on heaving soils.
TISE piles bear the load of heavy stone and light frame houses equally well, without shrinking.
The purpose of the grillage in the TISE foundation is to connect all the TISE piles into a single structure. It does not contact the ground, evenly distributing the load from the house between the piles.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the TISE foundation include:
- low cost;
- no need to use heavy construction equipment;
- autonomy of work during construction: to perform technological operations, no connection to the electrical network is required;
- high speed of construction and minimal labor costs;
- the possibility of independent construction by individual developers who do not have experience or special skills;
- ease of installation of utilities even at a fully constructed facility.
Disadvantages of foundation technology on TISE piles:
- this construction method cannot be used in swampy areas, waterlogged and silty soils;
- using only manual labor: this makes the construction process very difficult on rocky and hard soils. At the moment, the TISE foundation expander is being produced, which allows you to work with a gas drill;
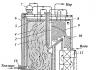
- A cover made of several layers of roofing material, PVC film or galvanized steel is provided along the entire length of the wells to prevent the piles from being pushed out under the influence of swelling of the soil during frosts (nothing will harm the foundation if the soil slides over the protective cover).
- a reinforcing cage is installed in the wells in the form of connected reinforcement rods, with the rods extending above the poured piles to the height of the future grillage - the reinforcement will subsequently serve as a connecting link between the cast-in-place pile and the grillage, and will also prevent possible rupture of the foundation as a result of soil heaving, and in the case of tying the piles With other materials, reinforcement rods removed are used to secure the strapping or are removed.
- The pile foundation is poured with “heavy” concrete (with quartz sand or crushed rock), filling occurs continuously in each well in layers, the concrete is compacted by bayonet.
Walls made of formwork using TISE technology are reliable and frost-resistant, and the foundation has high strength of the load-bearing structure and durable operation on heaving and clay soils.
One of the most important advantages of the TISE construction technology is that almost every person, using a drill and formwork using the TISE technology, can build the walls and foundation of a house with their own hands without resorting to the services of professional builders. In this case, the house turns out to be capital and as financially accessible as possible, which will delight you for many years.
Over the 25 years of successful implementation of TISE construction technology, thousands of people have built their own houses.
For those who decided to build a foundation with their own hands
Foundation on TISE pillars - Choice No. 1 when planning the construction of a Foundation with your own hands.
The foundation on TISE pillars is a columnar foundation that can be used for the construction of houses (up to 3 floors), bathhouses, garages, massive fences, structures, etc.
When developing the foundation on TISE poles, the calculation was made that any person “who knows how to hold a tool in his hands” could independently, alone, build a foundation with his own hands, in the absence of electricity and without the use of construction equipment.
Moreover, at the lowest cost, because for the construction of the foundation
You will need sand, cement, crushed stone, reinforcement and related building materials.

To ensure the integrity of the foundation on heaving soils, it is better to use bored piles. This method allows you to reduce the cost of the foundation as a whole, due to the possibility of performing the work independently, without the involvement of construction equipment and construction crews.
The foundation on bored piles is made by concreting pre-drilled wells.
Drilling piles under the foundation can be carried out with a hand drill with a maximum diameter of up to 30 cm. We recommend using the TISE Drill. Thanks to the special arrangement of the cutting blades, drilling requires little effort. The required depth and diameter of the well are calculated based on the characteristics of the soil.
Further construction of pile foundations made of bored piles looks like this:
The poured foundation on piles can be loaded when the concrete has finally set.
What can we find on the Internet about foundations on bored piles?
"Bored piles
With this type of pile foundation, it is necessary to first drill wells into which the piles are laid and concrete is poured. This type of foundation installation on piles is most often used in the construction of multi-story buildings. Technical complexity, complex calculations and high cost of work are the disadvantages of foundations on bored piles."
Check out TISE technology! You will understand that foundations on bored piles are simple and cheap. Using the TISE Drill you can pour foundation piles yourself. We make foundations on piles an affordable and budget-friendly solution for construction. The time for constructing a pile foundation using TISE technology is limited only by the rate of hardening of the concrete solution. You can purchase the necessary equipment in our online store. A foundation on piles is simple, affordable and reliable.
Are you planning to build a foundation on pillars? We recommend that you familiarize yourself with TISE technology. In our online store you can purchase a drill for self-construction of a foundation on pillars. TISE technology involves expanding the foundation column in its lower part, which significantly improves the quality of the foundation on the pillars. It is possible to build a foundation on pillars using TISE technology both with and without a grillage, which makes this technology universal.
If you are planning to build a foundation on piles, we suggest that you familiarize yourself with TISE technology. TISE technology allows you to build a foundation on bored piles either independently or with the involvement of builders. A distinctive feature of the foundation on piles using TISE technology is the expansion of the lower part of the pile, which significantly improves the characteristics of the pile foundation. The foundation on piles using TISE technology can be either with or without a grillage, this allows the use of TISE piles in almost any house project.
The desire to build your home cheaply and reliably is increasingly forcing developers to look for more efficient new construction innovations. Wood concrete houses, aerated concrete or foundations using TISE technology have long since come into the construction of low-rise buildings and have become commonplace. Foundation systems on TISE piles, which have increased load-bearing capacity, are slowly but surely gaining popularity in individual construction, often even where their use does not bring any particular benefits.
What is the TISE foundation and where is it used?
This is a technology borrowed from the field of industrial construction, which was developed for the construction of high-rise reinforced concrete structures in problem areas. Building a house on a foundation using TISE technology made it possible to solve a number of specific problems:
- To ensure the construction of a foundation with high load-bearing capacity with a minimum amount of excavation work, which improves the ecology in the area adjacent to the construction site;
- Make the house structure insensitive to any ground vibrations, for example, metro, trams and railway transport;
- Avoid destruction of the house frame due to soil heaving, especially for areas with a large depth of soil freezing.
For your information! The last point is most often the main argument in favor of using the TISE foundation.
The fundamentally universal foundation using TISE technology is not much different from any other pile support systems. The main and main difference lies in the design of the TISE pile itself. It resembles an inverted screw with a countersunk head; at the bottom of the pile there is a hemispherical expansion, with a diameter twice the cross-section of the main shaft.

The TISE pile, unlike other support options, is cast in the ground from a concrete mixture, which significantly simplifies the technology and minimizes the cost of transportation and installation of foundation supports. But for casting, you will need to make a well with a depth below the freezing point, and this, for example, for the Moscow region can be 120-150 cm. In practice, the pouring depth is carried out in the region from 150 to 250 cm. There are few reasons for such wastefulness, but they exist. Firstly, the concrete body of the TISE pile in the ground contributes to deeper freezing of the soil, so they try to bury the support lower; secondly, the warmer lower layers of soil with temperatures from +3 o C to +5 o C warm up part of the concrete structure and reduce the risk its destruction.
DIY TISE foundation
In addition to a lot of positive aspects, universal foundations using TISE technology have quite a lot of nuances and conditions for using the pile system. For example, the TISE foundation, unlike the tape version, does not forgive mistakes; miscalculations and technology violations are much more expensive than in the classic version. Therefore, before starting work, you will need to calculate the TISE foundation.
Estimated calculation option for the number and size of TISE piles
There are many recommendations and techniques, including practical ones, based on an accurate geological study of the soil and the choice of method for reinforcing the foundation. But, without experience and full engineering knowledge, it is better not to use complex methodological recommendations, but to estimate the number of TISE piles and the step of their installation.
The procedure for assessing the parameters of a TISE pile foundation:
- Based on the sketch and accurate data on the geometric dimensions of the house, materials of walls, ceilings, roof frame, roofing material, the weight of the house is calculated as scrupulously as possible. To the obtained value it is necessary to add the weight of furniture, equipment and the mass of snow cover of maximum thickness;
- It is necessary to drill at least three points of the pit, one meter deep, in the area where the construction of the TISE foundation is proposed, classify the soil and determine the load-bearing capacity of the pile in tons using reference data from the table;
- Next, we divide the weight of the building by the tabular standard for the specific size of the support foot of the TISE pile. We get the number of TISE supports. It remains to divide the length of the foundation strip by the number of supports, and we obtain the required pitch between the piles.
Advice! The distance between the TISE supports depends on the thickness of the grillage; for a section of 30 cm, an average step value of 1.2-1.5 m can be taken.
In addition to the pencil method of estimating the number of piles, you can resort to specialized programs that allow you to work as accurately as possible with the parameters of the TISE foundation. Most often, this method is used if the construction budget is limited, or documentary detail is needed when drawing up an estimate for the construction customer.
Preparation for installation of TISE foundation piles
The most difficult stage in the construction of foundations using TISE technology is drilling pits or wells for piles. Today, almost the entire volume of drilling for TISE piles in the private sector is carried out using Tise-F hand drills. The work is hard, productivity is highly dependent on the density of the soil. Before you start drilling holes, make a standard marking of the foundation on the site, fill out the TISE pile lines and drilling points. The soil removed to the surface can be placed in a wheelbarrow or on a tarpaulin; during breaks, it can be removed along with debris and pieces of turf.

- First, we drill at all points where the piles are located to a depth of about 80-90% of the calculated value. Preliminary drilling is best done with a tool without a side attachment, this makes it easier to work;
- A couple of buckets of water are poured into each drilled well, and after an hour and a half they begin to form an expansion or cavity under the support heel of the TISE pile. Soaked soil will be easier and faster.
Important! When drilling, try to control the drilling vertical as much as possible; when installing a reinforcing frame made of steel rod, this will allow you to correctly install the reinforcement in the well.
With a large diameter of the heel, it is quite difficult to select soil from the cavity, but this must be done at any cost. You can add water or rotate the drill with jerking movements - the main thing is that the blade or plow of the tool carefully cuts out the cavity of the required size.
Casting piles using TISE technology
Before pouring concrete, you will need to perform two more important operations - install waterproofing and reinforcement. The quality of the formation of the side surface of the pile and the resistance of the support to freezing in a humid environment depend on the quality of the waterproofing layer. There is no need to explain the importance of correct installation of reinforcement; this is the key to the strength of the TISE pile, which works both in compression and in tension.
For waterproofing, a standard sheet of roofing material is used. A sheet one meter wide is cut to the size of the depth of the well plus the removal of waterproofing above the ground surface. The workpiece is rolled into a pipe along the diameter of the well, and the seam in the upper part of the insulation is sealed with mastic. The amount of waterproofing above the ground must be adjusted to the size of the bottom of the foundation strip plus 3-5 cm. The waterproofing is lowered into the well and fixed with spacer slats.
The reinforcing frame of the foundation pile is most often welded in advance from a 10-12 mm reinforcement bar with side jumpers. The lower ends of the rods are connected and reinforced with welded elements made of thicker metal. The upper ends extend above the cut of the TISE pile to the height of the foundation or grillage. All that remains is to install the frame in the well and align its position so that the ends of the rods are in the same vertical plane with the threads of the horizontal reinforcement of the foundation.

This method of manufacturing the TISE foundation frame does not provide a full-fledged heel of the TISE pile, and this is one of the most significant disadvantages of the technology. In some cases, the frame is made up of separate rods with ends bent to the side. After installing 6-8 rods in the well, they are deployed and oriented so that the bent parts of the reinforcement diverge radially in different directions, thereby strengthening the heel of the TISE pile. The axial part of the TISE pile is strengthened by installing a conventional welded frame of four rods with ligation with peripheral elements.
Before pouring concrete into the well, the upper part of the waterproofing, protruding above the surface, is put into a rigid collapsible form made of wood or metal and covered with sand. For a standard TISE pile with a shaft diameter of 25 cm, 60 to 90 liters of solution will be required, depending on the embedment depth. The volume is considerable, so it will be most convenient to use a manual or electric concrete mixer. In addition, this will allow for good mixing of all components of the solution, which means uniform shrinkage of the foundation and a minimum of surface defects.
It is most convenient to fill through a horn or sleeve. After filling more than half of the pile cavity, it is necessary to casing the solution. To do this, we take a crowbar and tamp the solution, trying to completely fill all the voids in the area of the heel of the TISE pile. Similarly, we fill and compact the second half of the foundation support cavity.
Advice! When pouring, control the level of the foundation concrete so as not to cover the ends of the reinforcement that are to be tied to the foundation tape.
Specialists involved in consultations on the arrangement of the TISE foundation believe that with normal viscosity of the solution, part of the cement with water will flow into the bottom of the sole and form a clay-cement cushion. Thus, the bearing capacity of TISE foundation piles should increase by at least 40-60% of the calculated value.
Assembly of the TISE foundation
In the classic version, the foundation of the yew is built in the form of a grillage, resting on piles at a height of 5-10 cm above the ground level. This method of constructing a TISE foundation allows you to protect the concrete mass from moisture and soil heaving.
The assembly of the supporting strip of the grillage occurs according to a scheme similar to the casting of a strip foundation. Before starting to assemble the panel structure for casting the foundation support mass, the space between the heads of the TISE piles must be filled with sand to create support for the bottom formwork panel.
Next, the lower and side walls of the formwork for the future foundation are installed on the sand and gravel backfill; the wooden structure must be carefully leveled horizontally so that when pouring the solution, the moving mass of concrete does not flow to one side. The sides are reinforced with wooden stakes and supports. For a small frame house of 5x8 m, it will be enough to make a foundation grillage 30 cm high and 25 cm wide.
At the next stage, it is necessary to lay film or roofing felt waterproofing on the bottom of the formwork; the edges of the roofing felt insulation of TISE piles are cut with a “chamomile” and run under the film layer of the foundation formwork.
The most labor-intensive stage in casting a foundation strip is the correct laying and tying of reinforcement bars. A 10 mm steel rod is used to reinforce the grillage and foundation. To strengthen the foundation, a lower layer of reinforcement of four threads is laid at a distance of 3 cm from the bottom and a similar top layer.
Tying the threads of the foundation reinforcement can be done according to the diagram suggested in the figure.
While pouring the tape solution, anchor bolts or fasteners are embedded into the concrete body, with the help of which the base of future walls will be attached, covered with film, and kept for at least two weeks until the casting gains preliminary strength. In extreme heat during the first couple of days, it is necessary to spray the structure with water once a day.

Conclusion
The TISE foundation can be used for two and even three-story frame buildings. But we must take into account that an average building of 350-370 tons on soft soil will require at least a hundred TISE supports, which is quite difficult and time-consuming to do manually. In addition, unlike most foundation schemes, TISE supports require very careful sequential execution of all technological operations and good quality cement.
People who have already assessed all the pros and cons of building on their own most often single out one type of foundation - a support structure using TISE technology. The abbreviation TISE means: technology of individual construction and ecology. Using it, you can create a foundation for building a house without having any special skills.
The construction of a support structure using TISE technology will reduce the costs of construction and operation in the future by almost half. Construction of a foundation using this technology does not harm the environment, because the work performed is carried out using common materials.
Using new construction methods, TISE technology, some problems are solved:
- Premises are isolated from contact with materials. Effective ventilation can be used, which makes it possible to introduce displacement ventilation systems. Thus, there will be no stagnant zones in the house.
- It is possible to create a useful electromagnetic field.
- The supporting structure does not produce a high background radiation.
- The buildings are well insulated from radiation.
- The new energy saving system reduces energy consumption from heating systems several times.
- Environmental safety increases.
- Saving money.
It is quite profitable to install a strip foundation on columns using TISE technology, especially if you correctly calculate and mark the future foundation of the house. Creating this type of support does not require a lot of excavation work, and less concrete will be needed.
Creating a TISE foundation makes it possible to reduce costs and create a support in a short time; its construction does not require the involvement of additional workers.
 Typical view of TISE.
Typical view of TISE. Advantages and disadvantages of foundations using TISE technology
TISE is a pile-tape structure; the supporting structure is erected in the form of a square or rectangle on piles.
The concrete grillage that connects the piles does not touch the ground. This position of the foundation does not allow the soil to put pressure on itself at any time of the year.
Advantages of the TISE foundation
- Economically advantageous part of the building;
- Reliable design;
- Fast construction;
- Easy installation;
- Can be built in winter;
- Environmentally friendly design;
- Construction on seismically unstable soil is possible;
- You can build a support at different groundwater levels.
Components of the TISE foundation:
- Grillage made of reinforced concrete;
- Reinforced piles.
The lower part of the foundation pile is shaped like a hemisphere - this is a big plus, because... This design helps to increase the support area and improve load-bearing properties. This support design is used in the construction of different types of houses. Such a foundation does not shrink and is suitable for houses on a frame basis, as well as for the construction of stone houses.
The lower part of the pile in the form of a hemisphere has the property of resisting squeezing out of the ground, which can occur in heaving soils.
The disadvantage of installing a TISE foundation is the mandatory purchase of special equipment: drills and motor drills.
The strip part of the TISE foundation is called a grillage - it is made of reinforced concrete. This part of the support is poured at a certain distance above ground level. Due to the gap from the ground to the structure, heaving does not affect the supporting structure.
Foundation construction using TISE technology
The construction of a support using TISE technology does not require calculation of piles and precise installation location under the grillage.
 Construction of the foundation using TISE technology.
Construction of the foundation using TISE technology. The technology consists of several stages:
- The first step is to mark the outline.
- Then the wells are drilled and expanded.
- The next step is to reinforce the piles.
- Then the grillage is made.
- For residential developments, calculations are made by special organizations involved in projects, because it is necessary to examine the soil, make calculations and a design.
- Without preliminary calculations, you can build a TISE strip foundation for buildings such as a fence, bathhouse, veranda and garage.
In order to correctly carry out the work on the manufacture of a TISE pile foundation, several conditions must be met:
- The base of the piles must be below the freezing point.
- The base of the pile is made taking into account construction standards to fully resist soil heaving.
- A strong recommendation for installing a strip foundation, reinforcing piles and compacting concrete.
- The grillage should be at a distance of 10 to 15 cm from the ground.
- The width of the grillage should be less than the height.
- The grillage must be reinforced.

The disadvantages of this type of foundation are the large amount of work that must be performed not only at the stage of calculation and marking, but also at the construction stage. This is true if the work is performed by several people. Disadvantages also include purchasing or leasing special equipment, such as drills and motor drills.
Calculation of the foundation contour
Before starting the construction of the foundation, it is necessary to make markings and calculations. Marking is done using; peg, slats, fishing line, tape measure and water level.
First of all, slats are hammered in at the site of the future wall, with a margin of 2 meters, and a fishing line is attached to them.
To determine the first angle, step 1 m away from the batten and hammer a peg; a second peg is driven from it to the length of the wall. The slats are installed at the zero point of the TISE support structure; a water level is used to determine the top point of the grillage.
In order to mark the second wall you need to mark a right angle. The third and fourth walls are marked at a right angle, then edges 3 and 4 are simply connected to form parallel wall 2. Marking and calculation play an important role here!
The internal perimeter of the grillage is determined by a tape measure; the internal perimeter connected by fishing line is hammered into the width of the grillage from the outer edge. Then markings for the wells are made. You can determine the middle between the edges of the grillage and stretch the fishing line, and use it to mark the locations for the wells.

In the places where the marks are located, they dig holes on the floor of the bayonet and drill wells. Drilling is carried out with a special tool, the TISE foundation drill. This tool is manual and consists of a handle, a rod of two sections, a drill, a soil accumulator and a folding shovel. The depth is adjusted using a rod, the soil is taken up and loosened by a soil receiver, and the base of the well is expanded with a folding blade.
The downside to drilling wells is that after drilling the well, you need to expand its base, and for this you have to rebuild the drill. To optimize drilling, according to the advice of experts, several wells should be drilled and then expanded; this will take less time than rebuilding the drill.
During drilling, the drill and rod rotate, a folding blade is put on the rod and attached with a pin to the soil receiver. The blade is raised with a cord, and lowered under the pressure of its own weight. After expanding the wells, reinforcement and filling are carried out.

Pile reinforcement
- Piles are reinforced to increase their strength. After the reinforcing bars are poured with concrete, the pile becomes reinforced concrete.
- For reinforcement of piles, reinforcement with a diameter of 10-12 mm is used; for grillage, thinner reinforcement is used.
- Reinforcement and pouring of piles is done separately, since the grillage frame must be connected to the pile frame.
- The piles are poured in parts; after each part of concrete, a vibrator is lowered into the hole and compacted.
Pouring the grillage
- The piles are connected using a grillage. This way the load on the piles is distributed evenly.
- The formwork is installed using TISE technology. Waterproofing is fixed inside the formwork - this is necessary to keep the cement laitance in the solution.
- Sand is poured onto the bottom of the formwork and a frame made of reinforcement is installed, secured with a distance of 5-7 cm from the walls. The grillage is poured and compacted with a vibrating plate or deep-well vibrator.
- The poured foundation is left to harden, after which the formwork is removed and the sand is removed.